“`html
Effective Ways to Multiply Polynomials in 2025: Improve Your Skills Today!

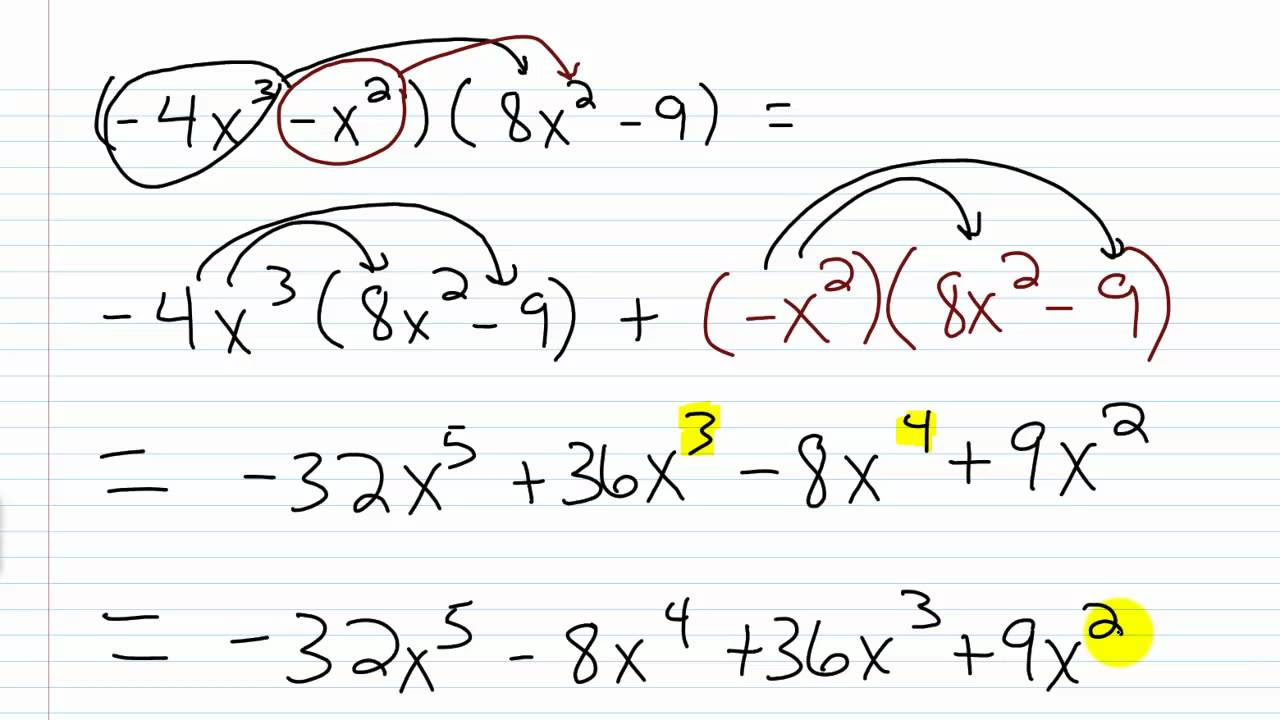
Multiplying polynomials is an essential skill in algebra that can come in handy in numerous mathematical applications. Mastering **how to multiply** polynomials effectively can simplify complex expressions and lead to successful problem-solving. This article will explore the best **methods for polynomial multiplication**, including examples and strategies to enhance your understanding of algebraic expressions. Whether you’re learning the basics or looking to refine advanced techniques, we’ve got you covered!
Understanding the Basics of Polynomial Multiplication
To effectively **multiply polynomials**, it’s vital to understand what they are. A polynomial is an algebraic expression that includes coefficients, variables, and terms combined using addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Depending on the number of terms, a polynomial can be classified as a **monomial**, **binomial**, or **trinomial**. Learning various **polynomial operations** is crucial to handling problems systematically and efficiently.
The Distributive Property in Polynomial Multiplication
The **distributive property** is one of the fundamental techniques for **polynomial multiplication**. This method involves multiplying each term of one polynomial by every term of the other polynomial. For instance, if we are to multiply (2x + 3) and (4x + 5), we distribute each term from the first polynomial over the second, giving us:
2x * 4x + 2x * 5 + 3 * 4x + 3 * 5 = 8x² + 10x + 12x + 15 = 8x² + 22x + 15. By practicing the distributive property with different polynomials, you will become more comfortable with **counting polynomial coefficients** and managing various polynomial terms.
FOIL Method for Binomial Expansion
The **FOIL method**, which stands for First, Outside, Inside, Last, is a specialized technique used primarily for multiplying two binomials. For example, let’s consider (x + 2)(x + 3). Applying the FOIL method results in:
- First: x * x = x²
- Outside: x * 3 = 3x
- Inside: 2 * x = 2x
- Last: 2 * 3 = 6
Putting it all together, the product is x² + 3x + 2x + 6 = x² + 5x + 6. Using the FOIL method is efficient for quick calculations in the polynomial multiplication process, especially for binomial expressions.
Visualizing Polynomial Multiplication
Visual aids can significantly enhance your understanding of **multiplying polynomials**. One popular method is the **area method**, which involves drawing rectangles to represent the terms of each polynomial. Each rectangle’s area corresponds to the product of the terms. For example, for (x + 2)(x + 3), create a grid where one side represents x + 2 and the other x + 3. The dimensions of each section are the products of the unique term pairs, visually demonstrating the distributive property while reinforcing the concept of the **polynomial degree**.
Common Mistakes in Polynomial Multiplication
While **polynomial multiplication** may seem straightforward, many learners make mistakes when distributing terms, especially in dealing with negatives or combining like terms. For example, when multiplying (3x – 4)(2x + 5), students often forget to distribute the negative sign when multiplying by the second binomial’s terms. Practicing common problems and identifying these errors can significantly improve your overall understanding and accuracy in polynomial multiplication.
Advanced Techniques for Polynomial Multiplication
Once you’ve grasped the basics, consider diving into more advanced **polynomial techniques**. These approaches provide deeper insights and allow for the simplification of complicated expressions.
Factoring and Analyzing Polynomial Identities
Understanding how to **factor polynomials** can streamline the multiplication process. For instance, applying the **factor theorem** involves factoring an equation into simpler polynomials, thereby making calculation easier. When you factor a polynomial before multiplication, you deal with smaller, more manageable expressions, further aiding in understanding polynomial identities and their relationships.
Polynomial Long Division
For higher degree polynomials, **multiplying polynomials** may require techniques like **polynomial long division** and **synthetic division**. These methods help in dividing polynomials more efficiently. Suppose you need to multiply (x² + 1) by (x + 2x + 4). Using these division techniques, one can simplify the multiplication of more complex factorable polynomials, turning cumbersome calculations into manageable steps.
Common Applications of Polynomial Multiplication
In applied mathematics, **polynomial multiplication** plays a crucial role in modeling real-world scenarios. From physics problems involving trajectory calculations to economics predicting growth, understanding polynomials allows one to use complex functions effectively. Identifying **roots of polynomials** and graphing these equations provides practical experience connecting theoretical knowledge with tangible results.
Resources for Polynomial Multiplication Practice
Practice is essential to mastering **multiplying polynomials**. A variety of resources are available for students seeking additional support, whether you desire structured lessons or self-paced exercises.
Online Tutorials and Video Guides
Video tutorials offer a dynamic method for learning **polynomial multiplication**. Consider subscribing to YouTube channels dedicated to algebra tutorials, which cover various topics including visual explanatory videos that demonstrate the concepts covered in this article. Platforms with interactive learning opportunities can also enhance your understanding of **algebra fundamentals** by providing visual techniques and examples.
Worksheets and Interactive Tools
Worksheets on **polynomial multiplication** are available in abundance online. Search for **practice problems”** that lay out straightforward and challenging questions across multiple levels of complexity. Engaging with these worksheets enhances your skills while providing opportunity for practical application. Tools such as online polynomial calculators can also assist in checking your work, allowing for hands-on learning.
Group Study and Tutoring
Collaborating with peers can often illuminate complex concepts. Organizing study groups can facilitate discussion on **algebra concepts**, helping each participant grasp intricate procedures related to polynomial multiplication. Alternatively, consider investing in tutoring for personalized attention, ensuring your understanding is comprehensive and tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Mastering **multiplying polynomials** is an indispensable skill in the world of algebra. From learning the **distributive property** and advanced techniques like long division to using diverse resources for practice, there are unlimited avenues for solidifying your understanding. Whether preparing for exams or enhancing your knowledge for real-world applications, actively engaging with these concepts will ensure you remain proficient. Utilize the resources available and keep practicing to elevate your algebra skills!
FAQ
1. What is the **area method** for multiplying polynomials?
The area method involves visualizing the multiplication of polynomials as areas of rectangles. Each term from one polynomial corresponds to a rectangle that measures the terms of the other polynomial, allowing you to calculate the products systematically. It provides a graphical representation of polynomial multiplication, making comprehensions easier.
2. How does synthetic division work in polynomial multiplication?
Synthetic division is a simplified form of polynomial long division, allowing for faster computations when dividing polynomials. This method eliminates the need for writing out all the terms and can provide insights into polynomial roots, making it an essential tool for understanding polynomial equations.
3. What should I remember while **factoring polynomials**?
When **factoring polynomials**, ensure you always look for a common factor in all terms first. Carefully group the polynomial, check for hidden binomials, and apply the difference of squares when necessary. This approach allows simplification for easier multiplication later on.
4. Why is the FOIL method primarily used for binomials?
The FOIL method focuses on the four specific products obtained from the two binomials. Each product corresponds to the unique combinations of the leading terms, ensuring a structured approach to multiplication. This method significantly simplifies the multiplication process compared to distributing each term individually.
5. Where can I find additional resources for polynomial multiplication?
Numerous online resources such as educational websites, video tutorials, and interactive tools can aid in learning polynomial multiplication. Many platforms offer free worksheets and practice problems to reinforce your understanding and help you learn effectively. Investing time in these resources can significantly improve your skills.
“`
