Effective Ways to Calculate Operating Income for Your Business in 2025
Calculating **operating income** is crucial for evaluating your business’s financial performance. This metric reflects the profitability of your core operations by considering revenue minus the total expenses directly related to the operation of your business. In this article, we’ll explore effective ways to calculate operating income, its significance, and how you can improve it for better financial health.
Understanding Operating Income and Its Importance
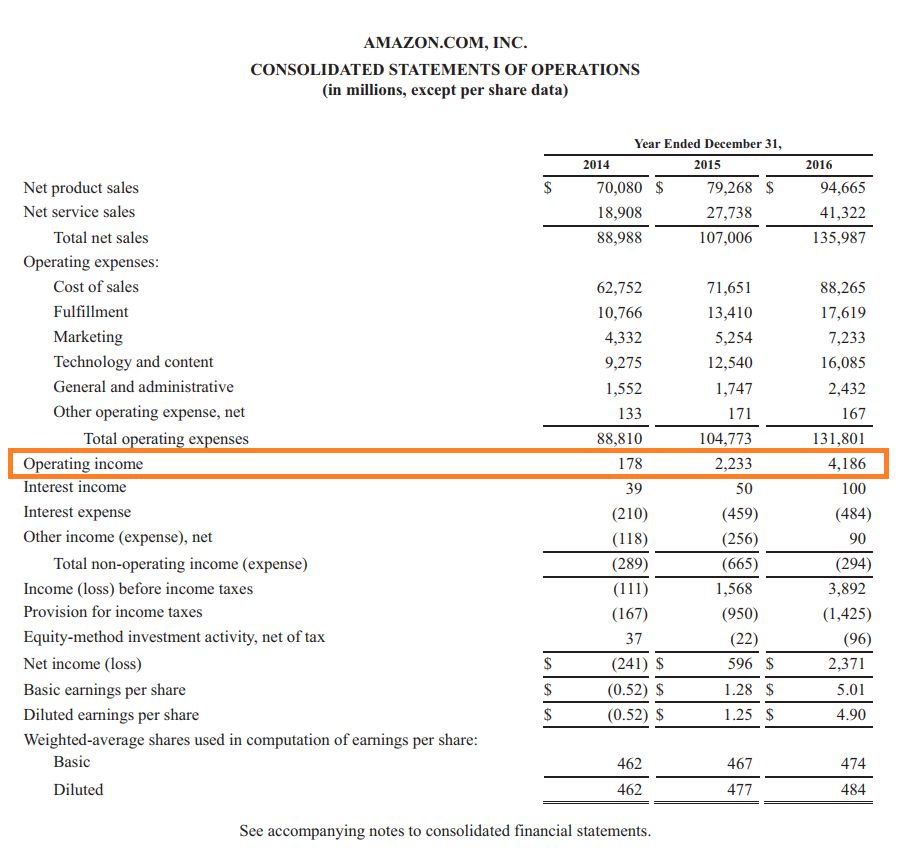
**Operating income**, also known as operating profit, is a key indicator of your company’s operational efficiency. By focusing on the income generated from core business activities, it excludes non-operational income and financial costs, providing a clearer picture of the company’s financial health. The **operating income formula** typically expressed as revenues minus operating expenses (including cost of goods sold and general administrative costs), allows business owners to assess performance without the impact of debt or taxes. Understanding your **operating margins** can help identify trends and optimize resource allocation.
Definition and Components of Operating Income
The **definition of operating income** involves calculating total revenues and deducting costs associated with the production of goods or services sold. The key components in the **income statement** include **net sales**, which represent total sales after subtracting returns and allowances, and **operating expenses**, which encapsulate costs like salaries, rent, and utilities. A thorough grasp of these components is essential for determining your business’s overall profitability and operational efficiency.
Importance of Operating Income in Financial Performance
Evaluating **operating income** is vital for any business as it helps in assessing financial stability without interim factors affecting profitability. Comparing **operating income trends** can provide valuable insights into operational efficiency, allowing businesses to make informed decisions. Moreover, monitoring operating income can highlight the effectiveness of management’s strategies on cost management and pricing, leading to improved **profit margins**.
Using Financial Performance Metrics for Evaluation
Financial performance metrics, such as the **earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT)**, are intimately tied to operating income. These metrics facilitate a comparative analysis across different periods or industry standards. By benchmarking your **operating profit definition** against industry norms, you can ascertain both strengths and weaknesses within your operational processes, thereby strategizing for increased profitability.
Calculating Operating Income in Practical Scenarios
There are several approaches to streamline the **calculation of operating income**, which are essential for accurately evaluating business performance. Accurately deducting expenses such as **cost of goods sold** and operational expenditures provides a robust understanding of how well the underlying business strategies are performing.
Step-by-Step Calculation Process
To compute operating income effectively, follow these steps:
- Identify **total revenue**: This includes all sales generated from business operations.
- Calculate the **cost of goods sold (COGS)**: This is the direct cost attributable to the goods or services sold.
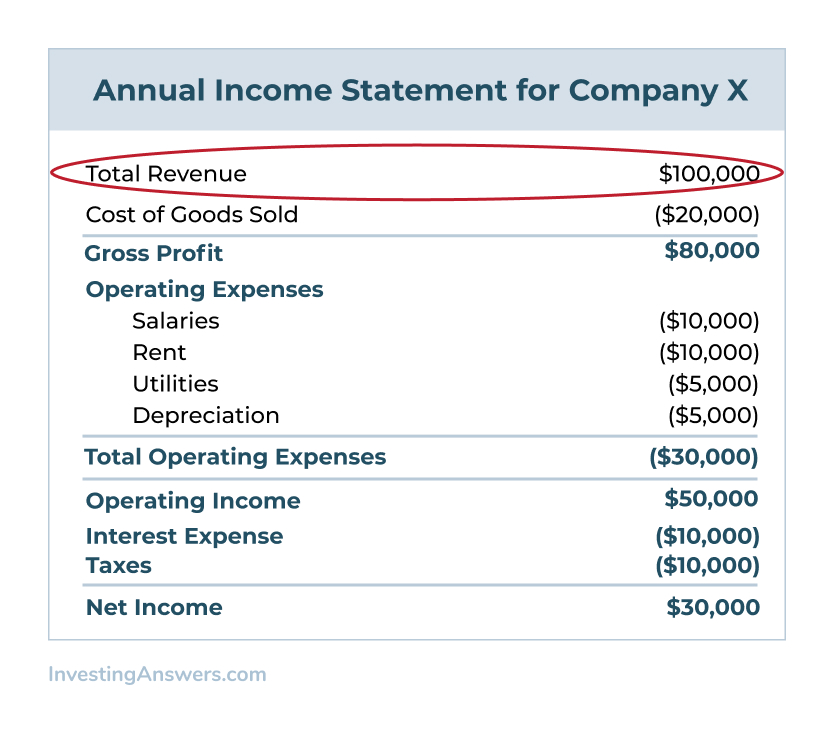
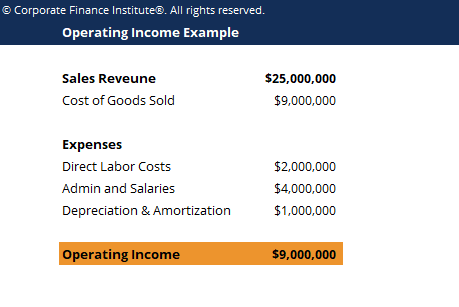
- Deduct COGS from total revenue to arrive at **gross income**.
- Subtract **operating expenses** (fixed and variable costs) from gross income. This results in your **operating income**.
For example, if your business generates $500,000 in revenue, incurs $200,000 in COGS, and has $150,000 in operating expenses, your calculation would be: $500,000 – $200,000 – $150,000 = $150,000 operating income.
Examples and Case Studies of Operating Income Calculation
In practical terms, businesses like retail companies often showcase **operating income** prominently in their financial reports because it reflects everyday operational performance. For instance, when analyzing a successful retail chain, one can observe how effective pricing strategies impact revenue generation while simultaneously monitoring how cost management strategies influence their operational effectiveness.
Impact of Revenue Recognition and Expense Reduction
Understanding how **revenue recognition** plays into the **operating income calculation** is paramount. By timing income correctly within accounting standards, businesses can present a more accurate view of their financial performance. Additionally, examining **cost management** techniques, such as streamlining supply chain expenses, can yield significant improvements in **operating profitability**. For instance, companies with effective inventory management systems often reduce direct costs, enhancing their ability to achieve sustainable profit.
Factors Affecting Operating Income and Business Decisions
Numerous factors can influence **operating income**, resulting in fluctuations that necessitate regular monitoring. Managing the balance between maximizing revenue generation and controlling costs is essential for sustaining **operational efficiency**.
Internal and External Factors Influencing Operating Income
Factors such as macroeconomic trends, consumer behavior, and industry competition significantly impact a business’s operating income. For instance, in periods of economic downturn, customer spending may decrease, directly affecting sales and, hence, operating income. Understanding how these external elements interact with internal processes such as workforce efficiency and supply chain reliability can foster a resilient business strategy.
The Role of Fixed and Variable Costs
Another crucial aspect affecting operating income is the distinction between **fixed costs** (expenses that remain constant) and **variable costs** (expenses that vary with production levels). A business with high fixed costs may find it challenging to maintain **profitability** during low-revenue periods, necessitating a focus on strategies to optimize operating income continually. By reviewing the proportion of these costs related to **cost structure modeling**, a company can adjust operations to improve overall profit margins.
Strategies for Maximizing Operating Income
Adopting effective strategies for increasing operating income is paramount for a business’s success. Some proven techniques include implementing better cost control measures, optimizing **operational efficiency**, and continuously refining the sales strategy to maximize **net revenue**. For instance, businesses employing a **contribution margin analysis** can target profitable product lines while eliminating ineffective offerings.
Key Takeaways and Conclusion
In outlining the importance and methodologies for calculating **operating income**, it’s clear that this metric serves as a foundation for financial performance evaluation. By understanding your revenue, cost structures, and expenses, your business can attain enhanced financial health and stronger **profitability analysis**. Regularly updating your financial projections and employing sound financial planning will ultimately lead to better decision-making and optimized operating income.
FAQ
1. How do you differentiate between operating income and net income?
The difference lies primarily in what is included in each metric. **Operating income** reflects income generated from regular business operations, excluding interest and taxes, whereas **net income** encompasses all revenues and expenses, including non-operating items such as taxes and interest. Understanding this distinction can help managers make vital business decisions based on core operational performance.
2. What common factors can negatively impact operating income?
Several factors can negatively influence operating income, such as increased competition driving down prices, rising costs of materials or labor, and unexpected operational disruptions. Awareness and analysis of these factors can help businesses mitigate risks effectively and implement strategies to sustain profitability.
3. Why is operating income considered a critical metric for financial analysis?
**Operating income** serves as a significant indicator of a company’s operational effectiveness and profitability. It provides insights into the efficiency of management’s operations and financial performance. Regular monitoring helps identify trends, assess cost management strategies, and inform future strategic decisions to enhance overall business performance.
4. Can you provide an example of a cost reduction strategy?
One effective cost reduction strategy is streamlining operations through automation. Implementing technology to handle repetitive tasks can significantly lower operational expenses. This reduction in costs directly enhances operating income, improving overall financial health and enabling a focus on revenue generation.
5. How does effective budget management influence operating income?
**Budgeting** plays a pivotal role in managing operating income by providing a framework to allocate resources efficiently. A well-structured budget allows companies to track expenses, adjust strategies when deviations occur, and reinforce the importance of maintaining profitability within projected parameters. Consequently, this vigilant management can significantly improve long-term operational outcomes.