How to Effectively Calculate Price Elasticity of Demand in 2025
The concept of price elasticity of demand is a key component of economic theory and plays a critical role in understanding consumer behavior. As we navigate the complexities of the market in 2025, it is more important than ever to grasp how to effectively calculate price elasticity and analyze its implications. This guide will delve into the various methods and principles surrounding the demand elasticity formula, providing practical insights for both students and professionals in economics.
Understanding Demand Elasticity
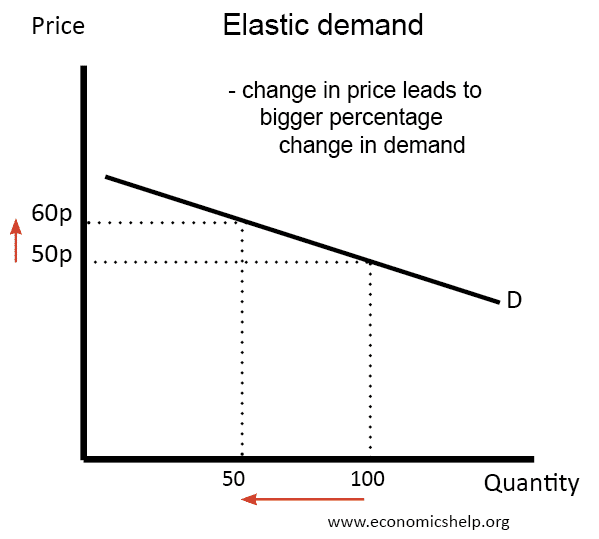
Demand elasticity refers to how sensitive the quantity demanded of a good is to a change in its price. The elasticity calculation method can yield varied insights depending on whether the demand is elastic or inelastic. Generally, if a small change in price leads to a significant change in quantity demanded, the demand can be considered elastic. Conversely, if quantity demanded changes only slightly when the price fluctuates, it is termed inelastic. Familiarity with these concepts sets the foundation for assessing market dynamics and consumer preferences.
Types of Elasticity
Various types of demand elasticity exist, with each offering unique insights. Elastic demand occurs when consumers are highly responsive to price changes. A classic example is luxury goods, where price increases may lead to a significant drop in sales, proving their demand sensitivity. On the other hand, inelastic demand characteristics are prevalent in necessities, where consumers will continue purchasing regardless of price increases. Recognizing whether demand is perfectly elastic, perfectly inelastic, or falls somewhere in between, helps businesses strategize pricing. Understanding these variations in demand responsiveness can inform pricing strategies and contribute to effective market positioning.
Factors Affecting Elasticity
Several factors influencing demand elasticity play a role in how consumers respond to price changes. Key determinants include the availability of substitutes, the necessity of the product, and the proportion of income spent on the good. For instance, if close substitutes are available, even a slight price increase can lead consumers to switch brands, indicating high elasticity. However, for essential items with few substitutes, demand remains stable despite price hikes. Market analysis must incorporate these factors, facilitating more accurate demand forecasts and tailored pricing strategies.
Real-world Applications of Elasticity
To illustrate the practical applications of elasticity in market analysis, consider a business testing a price increase on a popular soft drink. An elasticity calculation enables the business to predict changes in total revenue resulting from altered pricing. If the target market shows high demand responsiveness, higher prices may lead to decreased overall revenue, while lower prices could boost sales volume. Thus, proper measurement and understanding of elasticity can streamline pricing decisions and ensure business profitability amid fluctuating market conditions.
Methods of Calculating Elasticity
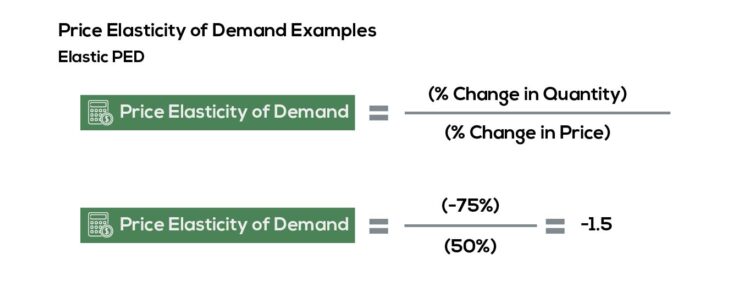
There are multiple methods for calculating elasticity, depending on the granularity of the data available and the specific needs of the analysis. The most commonly used method is the demand elasticity formula, which ratio divides the percentage change in quantity demanded by the percentage change in price. This basic formula serves as a robust foundation for further elasticity studies and can be applied in various contexts.
Point vs. Arc Elasticity
Two main methods employed for calculating elasticity include point elasticity and arc elasticity. Point elasticity provides a precise measurement at a specific price and quantity, often useful for smaller changes. In contrast, arc elasticity computes an average responsiveness over a range of prices and quantities, providing a broader contextual analysis. Each method has merit based on the specific scenario, and market analysts should choose the appropriate technique depending on available data and business needs.
Calculating Revenue Implications
Understanding the relationship between revenue and elasticity is crucial. When demand is elastic, a decrease in price can lead to an increase in total revenue as quantity demanded rises disproportionately. Conversely, when demand is inelastic, price increases may elevate total revenue, despite lower quantities being sold. This intricate connection emphasizes the need to thoroughly analyze the impact of price changes to inform pricing strategies effectively.
Practical Example of Elasticity Calculation
Let’s consider a practical example of a coffee shop introducing a new recipe and subsequently raising its prices by 20%. If the quantity demanded decreases from 1000 cups to 800 cups, we apply the demand elasticity formula for clarity. Here, the calculation would show a 20% decrease in demand as follows: \[ \text{Price Elasticity} = \frac{\frac{800 – 1000}{1000}}{\frac{1.2 – 1}{1}} \]. This elasticity measurement will determine how sensitive customers are to price changes, empowering the coffee shop with data to tweak pricing or develop promotional strategies.
Analyzing Consumer Behavior and Demand
Gauging consumer behavior is essential for accurate demand elasticity measurements. Factors impacting demand can include economic conditions, trends, and even seasonal preferences. Data interpretation methods such as surveys and historical sales analysis can offer insights into how consumers react to different pricing strategies.
Behavioral Economics and Elasticity
Behavioral economics lends further depth to understanding elasticity. Consumers often make purchasing decisions influenced by psychological factors, such as perceived value and urgency. During economic downturns, even common goods may see fluctuating demand elasticity as consumers reevaluate their expenditures. This perspective encourages marketers to diverge from traditional analysis, incorporating a broader range of raw data and consumer surveys to identify patterns and predict demand projections.
Elasticity and Price Strategy
Businesses should leverage elasticity findings to formulate effective pricing strategies. By understanding how consumer responsiveness varies across similar products or competitors, brands can adapt their tactics. Advanced elasticity analysis not only influences pricing but also drives marketing tactics, seasonal promotions, and adjustments in supply chains to correctly align with evolving consumer preferences.
Market Trends and Elasticity Impact
Finally, remaining aware of market trends and pricing influences can significantly affect demand metrics. Price wars or rising competitor pricing can increase overall consumer sensitivity, leading to unexpected shifts in demand elasticity. Businesses should actively monitor these trends, utilizing empirical research and market insights to dynamically adapt their strategies to maximize profitability.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding price elasticity of demand is crucial for aligning pricing strategies with consumer behavior.
- Elasticity can vary widely based on product type, necessity, and available substitutes, thus impacting demand sensitivity.
- Applying proper elasticity calculation methods can enhance revenue management and pricing accuracy.
- Consumer behavior insights enrich demand predictions and market strategies, proving essential for sustained business strategy.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between elastic and inelastic demand?
Elastic demand indicates that consumers are highly responsive to price changes, while inelastic demand means slight changes in price yield minimal shifts in quantity demanded. Understanding this distinction is vital for setting effective pricing strategies.
2. How do substitutes affect demand elasticity?
Availability of substitutes usually increases demand elasticity. If consumers can easily find alternative products, a small price increase could lead them to switch, emphasizing the necessity for businesses to monitor competitor pricing.
3. What is unitary elasticity?
Unitary elasticity occurs when a change in price results in a proportional change in quantity demanded. It’s an essential concept to master as it marks the point where total revenue remains constant despite price fluctuations.
4. How can businesses forecast demand elasticity?
Businesses can use historical sales data, market surveys, and consumer insights to effectively forecast demand elasticity. These methods allow for more accurate predictions of consumer behavior and potential revenue impacts.
5. Why is understanding price elasticity important for businesses?
Grasping price elasticity enables businesses to make informed decisions on pricing strategies, promotional tactics, and inventory management, leading to optimized profits and enhanced competitiveness in fluctuating markets.
img {
display: block;
margin: auto;
max-width: 100%;
}