How to Start Windows 10 in Safe Mode for Effective Troubleshooting
Booting Windows 10 in safe mode is often a crucial step for users facing various system issues. In this guide, we’ll delve into how to start Windows 10 safe mode along with the various options and methods available to troubleshoot Windows 10 boot issues. Understanding how to enable safe mode in Windows 10 can significantly enhance your ability to resolve problems and restore functionality to your system.
Understanding Windows 10 Safe Mode Options
When you encounter an operating problem, **accessing safe mode Windows 10** is essential for diagnosing and resolving issues. Each safe mode option caters to different user needs and situations. For instance, **Windows 10 safe mode options** primarily include Safe Mode, Safe Mode with Networking, and Safe Mode with Command Prompt. Safe Mode is the basic mode that loads only essential system files and drivers, which helps in identifying issues related to third-party software or drivers. Conversely, Safe Mode with Networking enables your network drivers and software, making it suitable for troubleshooting internet-related issues.
Safe Mode vs. Normal Mode
Understanding the difference between safe mode and normal mode is vital. While normal mode runs all system functions and applications, **boot Windows 10 in safe mode** loads a minimal set of drivers and services. This limited functionality allows users to troubleshoot issues stemming from problematic software or drivers without interference from normal operations. For example, if a software application causes conflicts leading to crashes, safe mode can prevent it from running, thus providing a stable environment to identify and resolve the issue.
Navigating Advanced Startup Options Windows 10
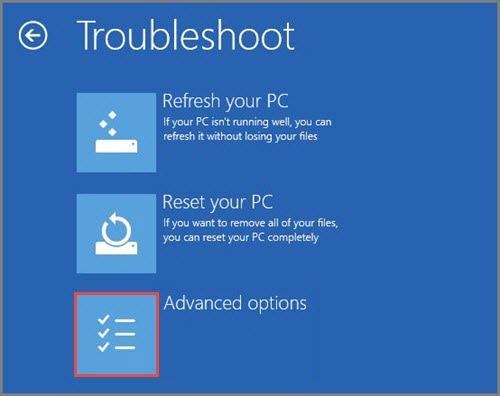
Accessing **advanced startup options Windows 10** can be achieved through settings. To reach these options, navigate to the Settings app and select Update & Security followed by Recovery. Under the Advanced Startup section, choose Restart now. This will allow you to select Troubleshoot, then Advanced options, where you can find various options to restart in safe mode. Utilizing these options, you can customize your boot settings to best address your troubleshooting needs.
Types of Safe Mode in Windows 10
Windows 10 features three types of safe mode that can help you depending on the problem at hand. The first one is the standard Safe Mode, which is primarily used for basic troubleshooting. The second option, Safe Mode with Networking, is useful if you need internet access—for example, to download drivers or troubleshoot further online while in this mode. Lastly, Safe Mode with Command Prompt replaces the standard desktop with a command interface, allowing experienced users to issue troubleshooting commands directly.
Knowing these types can streamline your **troubleshoot Windows 10 boot issues**, ensuring you take the correct troubleshooting approach for your specific problem.
How to Boot Windows 10 in Safe Mode
To effectively utilize safe mode, you must first learn **how to start Windows 10 safe mode**. There are several methods, each suited for different situations. Below, we discuss various techniques, particularly focusing on modern and traditional approaches to entering safe mode.
Using the F8 Key Method
The traditional method to start **Windows 10 safe mode** is by using the F8 key during boot, although it is often disabled by default in newer versions. To utilize this method, first, ensure that you disable Fast Startup. If successful, pressing the F8 key during the boot will bring up the boot menu where you can select safe mode. This method is straightforward and doesn’t require navigation through the system settings once enabled.
Accessing Safe Mode via System Settings
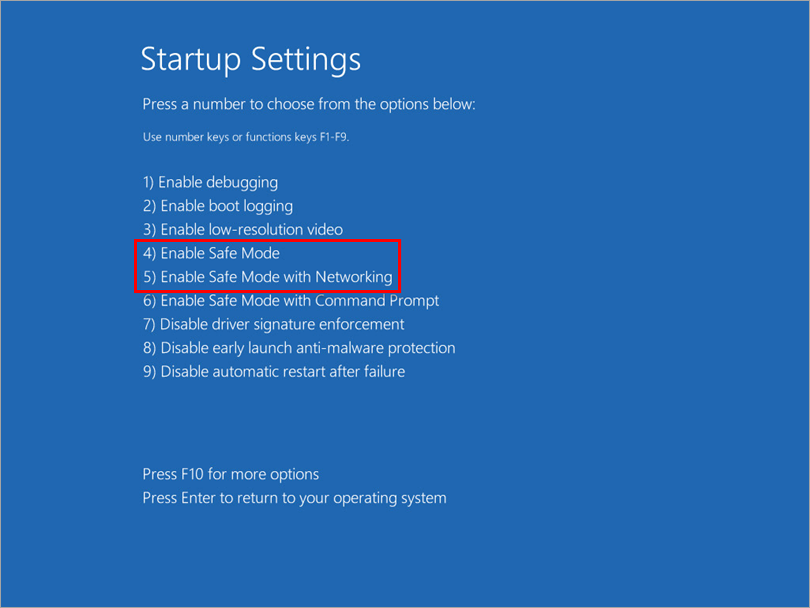
Another intuitive way to enter **Windows 10 safe mode** is through System Settings. Go to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery. Here, under the “Advanced Startup” section, select **Restart now**. After rebooting, choose Troubleshoot, then Advanced options, and finally Startup Settings. Hit **Restart**, and you’ll be presented with multiple options, including various safe mode configurations.
Using Command Prompt to Enable Safe Mode
For users comfortable with command-line interfaces, enabling **safe mode with CMD** can be effective. Open Command Prompt as administrator and type the command bcdedit /set {default} safeboot minimal for basic safe mode, or bcdedit /set {default} safeboot network for safe mode with networking. This method can be particularly beneficial when typical GUI navigation proves troublesome.
After diagnosing your issue, you can return to normal boot settings by typing bcdedit /deletevalue {default} safeboot.
Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues in Safe Mode
After entering **safe mode startup Windows 10**, the next step is to dive into troubleshooting. This environment is designed for problem-solving and recovering your system, allowing users to deal effectively with software conflicts, driver issues, or malware removal. Utilizing safe mode’s limited boot-up approach can help isolate the issues affecting your system performance.
Address Software Conflicts
Once in safe mode, the **Windows 10 troubleshooting** starts with identifying problematic software. Investigate third-party applications that may be causing conflicts. Uninstall abnormal entries through the Control Panel or use System Restore to revert back to a previous state before the issue emerged. This will eliminate faulty software without affecting your entire system setup.
Check for Faulty Drivers
Drivers are frequent culprits in system malfunctions. In safe mode, utilize the Device Manager to review and uninstall conflicting drivers. Right-click the Start button and select Device Manager, then identify any drivers marked with a yellow exclamation point. Uninstall or update these drivers to restore functionality following driver malfunctions.
Recovering and Backing Up Data
Utilizing **Windows 10 safe mode to recover** files is a significant advantage. During this phase, important documents can be copied from problematic installations to external storage or cloud services, ensuring no valuable data is lost. Be cautious, however, to avoid backup of potentially harmful applications that might recreate issues upon reinstallation.
Key Takeaways
- Learning how to access and utilize safe mode is vital for troubleshooting Windows 10 issues effectively.
- Different safe mode options cater to various scenarios regarding system performance and recovery.
- Methods such as using F8 key, system settings, or command prompt are essential techniques for booting into safe mode.
- Diagnosing software conflicts and faulty drivers during safe mode can lead to effective problem resolution.
- Backing up crucial data within safe mode ensures data integrity regardless of operating system issues.
FAQ
1. What should I do if Windows 10 won’t boot into safe mode?
If you’re struggling to boot into safe mode, consider accessing the Windows 10 recovery environment. You can do this by refreshing your PC or using installation media to repair your setup. This process often helps to bypass underlying issues preventing successful entry into safe mode.
2. Can I run updates in safe mode Windows 10?
While **running Windows updates in safe mode** is typically not possible due to the restricted environment, it’s often beneficial to restart your system afterward to apply updates when in normal mode. Consider checking for updates after resolving conflicts using safe mode.
3. How do I disable safe mode in Windows 10?
To disable safe mode, you can reboot your PC without the command-line option. Alternatively, you could reset your boot configurations to the default settings using CMD or through the System Configuration tool.
4. What are the limitations of Windows 10 safe mode?
**Safe mode** limits access to certain drivers and functionalities, restraining features like network connectivity (in standard safe mode). Consequently, certain applications may not operate as they would normally, making it a purely diagnostic environment.
5. How can safe mode assist in removing malware from Windows 10?
Booting into **safe mode without networking** helps in preventing malware from launching during startup, allowing users to run antivirus scans or remove malware effectively. Use this setting to give your malware removal tools the best chance to remove threats without interference.
6. Is there a difference between safe mode and safe mode with networking?
Yes, **safe mode with networking** includes drivers that allow network support, making it suitable for situations where you might need internet access during your troubleshooting process, such as downloading updates or drivers.